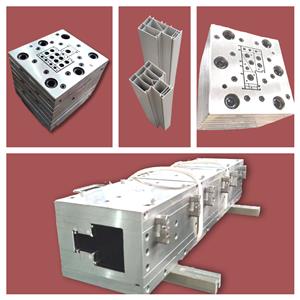
O plástico PVC, a construção do molde de extrusão, revela o véu para você
Existem duas formas de moldes comumente usadas: moldes escalonados de placa e moldes gradientes de seção transversal. O caminho do fluxo do molde escalonado da placa muda em etapas, que é feito de vários modelos de boca conectados em série. Cada placa é usinada em um formato de contorno correspondente, que muda gradualmente do formato redondo da entrada para o formato de saída desejado. Existem chanfros na entrada de cada bloco para completar a transição de uma forma para outra. Este tipo de custo de processamento de molde é baixo, o canal de fluxo não é idealmente simplificado e geralmente não precisa ser usado como perfil principal. O corredor do molde gradiente de seção é simplificado, não pode haver zona de retenção do material no corredor, o fundido é distribuído gradual e precisamente para cada seção do formato de saída do círculo na entrada, e a velocidade é aumentada constantemente para o velocidade de saída necessária e a velocidade de cada ponto da seção é a mesma. Para perfis plásticos de PVC com núcleos de molde complexos, o núcleo do molde é integrado à placa de suporte, alguns são fixados à placa de suporte por pinos e parafusos de localização e alguns são embutidos na placa de suporte por incrustações apertadas. Não pode ser facilmente desmontado durante o uso, pois é demorado para remontar e depurar. A derivação do fundido também é realizada de duas formas: no cone de derivação e na seção de compressão. O molde gradiente de seção pode ser usado como molde de perfil principal. O molde de extrusão de perfil de plástico PVC é a parte central da linha de produção de extrusão, que inclui matriz de boca (também conhecida como cabeça de matriz), molde de modelagem, tanque de água de resfriamento, etc. de um flange, e o anel de aquecimento, a placa de aquecimento, a fonte de alimentação e o termopar estão conectados. O molde de modelagem e o tanque de água de resfriamento são fixados à mesa de modelagem com parafusos, e o tubo de água e o tubo de gás são conectados. A estrutura básica da matriz de extrusão é geralmente projetada como uma estrutura de múltiplos modelos empilhados e montados. Portanto, o canal de fluxo de toda a matriz é formado pela conexão de um dos canais de fluxo em cada peça do gabarito, na frente e atrás. A placa é posicionada e fixada com pinos e parafusos para formar uma matriz de extrusão monolítica. A situação básica é: a seção de fluxo constante da matriz de extrusão é frequentemente composta por uma placa perfurada e a metade frontal do pescoço, e a metade frontal e a segunda metade do pescoço também são projetadas como dois modelos, o pescoço e o placa de transição do pescoço. Também é possível não usar uma placa porosa, mas projetar a metade frontal do canal de fluxo do gargalo em um canal de fluxo cilíndrico para estabilizar o fluxo. A seção dividida da matriz de extrusão começa na segunda metade do pescoço e inclui o cone dividido, a placa de suporte dividida e a placa retrátil. A placa retrátil pode ser dividida não em uma única fôrma, mas junto com a placa pré-formada - uma fôrma. A seção de formação da matriz de extrusão envolve os seguintes modelos: placa de cavidade (também conhecida como placa pré-formada), modelo de boca (também conhecido como placa de formação) e núcleo (também conhecido como núcleo de molde). Para matrizes de perfil mais simples, a placa pré-formada é combinada com o molde de boca em uma única fôrma. 1. Pontos-chave do projeto da seção transversal do produto O ponto-chave do projeto do produto de perfil de plástico PVC é que a espessura e a forma de cada seção devem ser distribuídas simetricamente, de modo que o fluxo de material no cabeçote da máquina seja equilibrado, o resfriamento possa ser uniforme , e a pressão tende a ser equilibrada. De modo geral, a espessura máxima da parede e a espessura mínima da parede da mesma seção são diferentes < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1